Lab Orchestration: The key to scalable, intelligent lab automation


In today's labs, simply having automation solutions is not enough. As the complexity of instruments, workflows, data streams, and team responsibilities increases, the real challenge lies in coordination, ensuring all these moving parts work together seamlessly. This is where laboratory orchestration plays a crucial role.
Lab orchestration acts as the connective tissue that brings structure and coordination to your lab’s entire automation ecosystem. It goes beyond scheduling instruments or triggering protocols—it involves synchronizing devices, data, people, and processes in real-time across the entire lab environment.
Lab orchestration supports the full spectrum of lab work, from manual and semi-automated to fully automated tasks. If you've ever questioned how lab orchestration fits into achieving better results, read on for a deeper understanding of how orchestration is shaping efficiency in modern labs.
What Is Lab Orchestration?
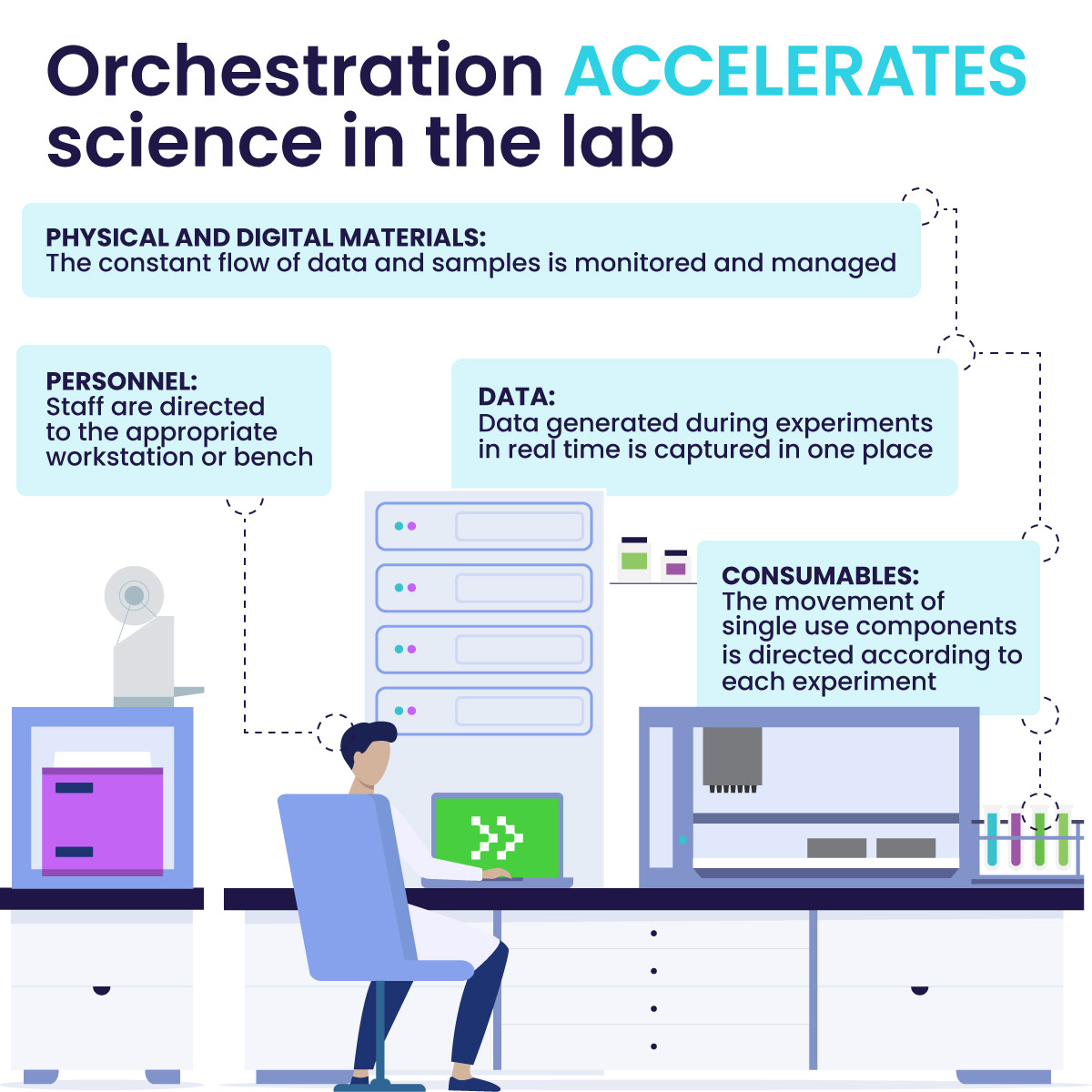
At its core, lab orchestration synchronizes instruments, workflows, and teams to streamline complex lab operations. This approach integrates devices, data, workflows, and lab personnel under a unified control layer. Some key orchestration components are:
Device Coordination
Modern labs utilize a variety of instruments from different manufacturers, each with unique interfaces, timing constraints, and software dependencies. Laboratory orchestration software synchronizes communication between these devices, ensuring they operate in the proper sequence and context. This coordination eliminates manual handoffs, reduces downtime, and maximizes the value derived from existing equipment.
Workflow Automation
Orchestration aligns multiple protocols and instruments into an interconnected, automated workflow that spans from sample preparation to data reporting. Orchestration enables multi-step processes to run seamlessly from start to finish without interruption. Instead of managing each device, or even each workcell, separately, orchestration allows you to define and execute complex, multi-step procedures with minimal intervention. The result? Greater consistency, faster turnaround, and fewer manual errors.
Data Handling
Data is generated at nearly every stage of the lab process, but without orchestration, this data is often fragmented or siloed. Orchestration centralizes data capture and integrates it with scheduling and execution. That means researchers can track results in context, generate insights more easily, and move toward closed-loop decision-making with confidence.
Every instrument interaction and manual touchpoint is passively recorded with timestamps and metadata, giving teams a full traceable history—ideal for audit readiness and process optimization.
People & Task Management
Humans are essential in lab workflows. Orchestration ensures that people and machines work in harmony by assigning the right tasks to the right individuals at the right time. It enhances visibility into task status, facilitates smooth data handoffs, and helps ensure compliance and accountability throughout the working process.
Orchestration systems can also help track consumable usage—from pipette tips to reagents—ensuring accurate inventory, minimizing waste, and maintaining compliance with lab protocols.
Benefits of Lab Orchestration
With a lab orchestrator tool to choreograph workflows, scientists can focus on what’s most important: designing the next experiment, interpreting data, and making the next big discovery.
Here are some other ways that lab orchestration can help:
- Orchestration protects data and sample integrity throughout the workflow, increasing the reliability and reproducibility of the results.
- Orchestration bridges the digital gap between systems, supporting complex integrations involving multiple workstations, transportation systems, and robots.
- Orchestration reduces the risk of human error and catches mistakes so operators can correct them.
- Orchestration manages consumables and reagents efficiently to reduce lab waste.
Lab Scheduling vs. Lab Orchestration
Lab scheduling and orchestration are often used interchangeably, but they are not the same. Understanding the distinction between the two is critical for labs looking to transition from basic automation to intelligent, scalable operations.
Scheduling focuses on when tasks happen, and orchestration focuses on how all components work together. Think of it this way: scheduling assigns tasks to instruments or lab personnel on a calendar, while orchestration ensures that all elements—including devices, data, workflows, and teams—are working in sync toward a common outcome.
How They Compare
| Feature | Lab Scheduling | Lab Orchestration |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Task timing and resource allocation | Full workflow integration and coordination |
| Scope | Isolated devices or tasks | Entire lab environment (devices + people + data) |
| Adaptability | Dynamic within a single integrated workcell | Dynamic across the entire orchestrated system |
| Visibility | Limited to task status | End-to-end workflow visibility and context |
| Scalability | Simple instrument additions to a single workcell | Simple workcell additions to an entire lab |
Visualizing the Difference
You can think of scheduling as booking an airline ticket for a lab instrument, where each process operates independently of the others. In contrast, orchestration is more akin to conducting air traffic control at an airport, where each section (instruments, software, personnel) plays its part at precisely the right moment, all coordinated by a shared objective. That’s the true power of orchestration.
Real-World Example: Orchestration in Action
Automating Flow Cytometry Workflows
In high-throughput drug discovery labs, flow cytometry is a key tool for analyzing multiwell plates—but the traditional process often involves time-consuming manual steps that slow progress and introduce variability.
With Biosero’s Green Button Go (GBG) Orchestrator, this workflow becomes fully automated across the physical, logical, and data elements of the lab. Here's how orchestration enhances the process from start to finish:
- Device Integration: Robotic arms are programmed to automatically load and unload multiwell plates into BD flow cytometers, eliminating manual intervention.
- Data Flow: Data is captured and transmitted in real-time to the GBG Orchestrator software the moment plates are processed, ensuring continuous monitoring and analysis. This information can then be passed outward into a relevant AI model, into other critical lab software like Titian Mosaic, or into PowerBI for reporting purposes.
- Notifications: Researchers receive automated alerts upon completion of each analysis, enabling timely decision-making and minimizing downtime.
This orchestration not only accelerates screening but also improves reproducibility and lab scalability. It reflects Biosero’s goal of enabling seamless robotic integration in complex scientific workflows.
From Workflow Execution to Strategic Enablement
Lab orchestration software supports strategic decisions, not just task execution. It enables smarter decision-making across your organization by offering:
- Centralized visibility into all ongoing lab activities.
- Consistent, high-quality data capture across instruments and sites.
- Faster onboarding of new assays, instruments, or collaborators.
- Proactive infrastructure monitoring—so teams understand when issues are environmental (like a compressed air shutdown), not equipment failures.
Powering the Future: Orchestration and Emerging Trends
As labs evolve to meet the demands of faster discovery and more innovative science, orchestration is emerging as the critical enabler of intelligent automation. Biosero’s lab orchestration platform goes beyond task automation—it establishes the digital backbone needed to support cutting-edge scientific approaches and technologies.
By integrating instruments, software, and data across the lab, orchestration sets the stage for:
- Closed-loop science – Where experiments inform algorithms, and algorithms drive the following experiments automatically and continuously.
- DMTA workflows – Seamless transitions between each phase with orchestrated scheduling, data handoffs, and protocol execution.
Biosero doesn’t develop AI, but it enables labs to be ready for it. With orchestration, scientific teams can:
- Capture high-fidelity data with consistent metadata and traceability.
- Automate workflows that are responsive to algorithmic recommendations.
- Connect with external AI and analytics platforms through an open, modular architecture.
This orchestration-first approach is what powers scalable, intelligent labs—and lays the foundation for the next wave of scientific innovation.
The Future Is Orchestrated
Automation moves tasks forward. Orchestration advances science by integrating automation, instruments, people, software, and data into a cohesive, adaptive system.
Orchestration transforms static workflows into dynamic processes that can evolve in response to new discoveries, emerging technologies, and shifting goals. Biosero’s orchestration platform empowers labs to scale, adapt, and innovate—creating the infrastructure needed not just to automate, but to think, learn, and respond to variables in real-time.
Whether you’re managing a single workflow or coordinating multiple labs across locations, orchestration enables global visibility, centralized dashboards, and performance tracking at scale.
Ready to orchestrate your lab’s future? Discover how Biosero can help you build a more connected lab environment. Contact us today.


Want to automate smarter, not harder? Join the Biosero newsletter and stay in the loop with the latest lab automation strategies, success stories, and product updates.


