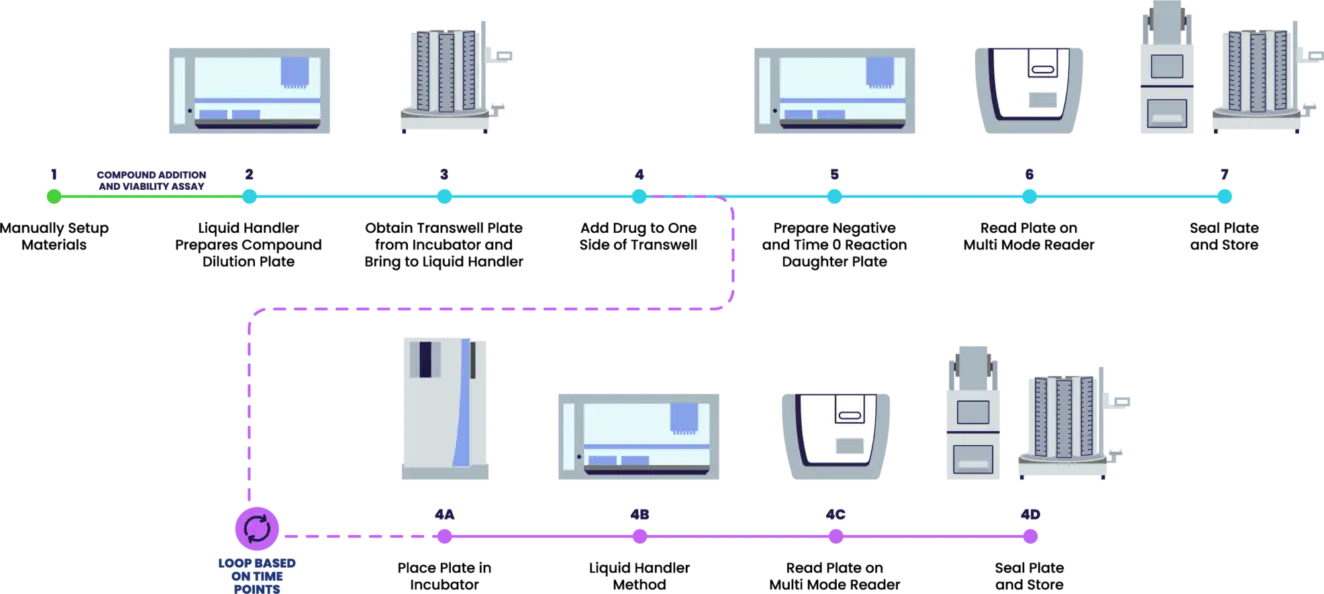
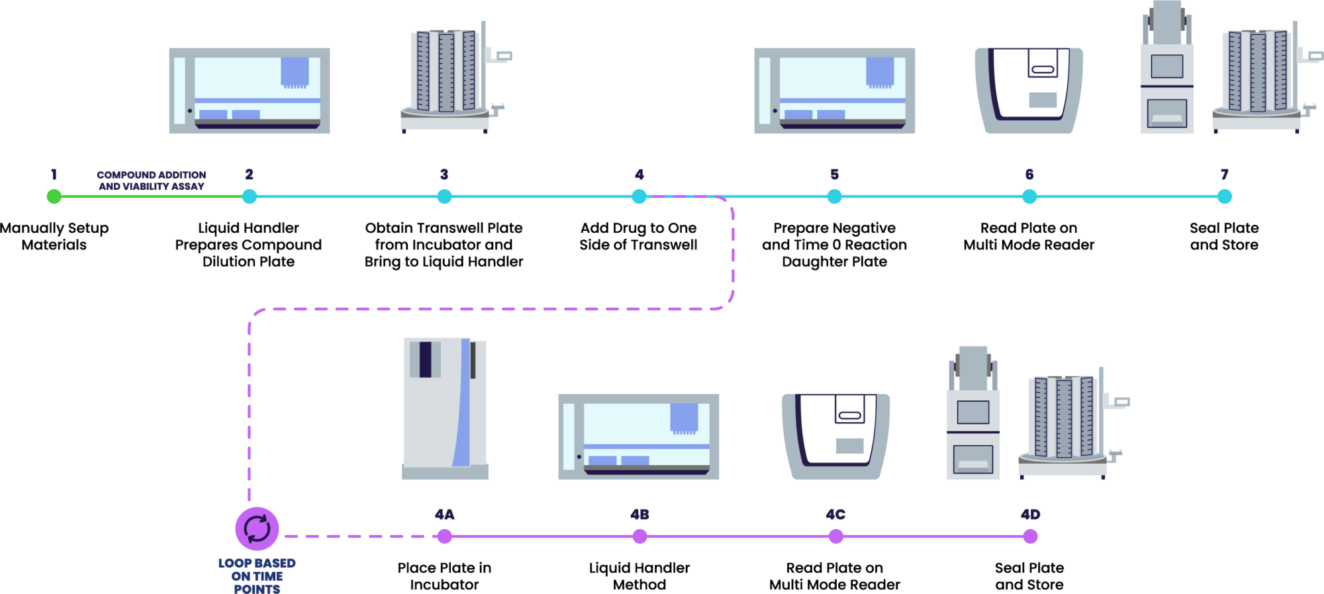
Automating DMPK - transporter assays
DMPK - transporter assays
Automating DMPK - transporter assays

The cell monolayer models are a popular Drug Metabolism and Pharmakinetics (DMPK) assay in predicting the in-vitro human intestinal permeability of a drug due to its morphological and functional similarity with human enterocytes. Adhesion or suspended cell lines that allow for first pass permeability assessments of xenobiotic mediated absorption or efflux analysis across tissue barriers are the main focus of the automated platforms described here.


Where automation makes a difference
Reproducibility
Research is reproducible when automation performs the same analysis and workflow consistently to produce consistent findings
Scalability
Modularity of workcell designs for components allows the lab to grow systems over time when increased throughput is required
Time savings
Automation can lead to long-term cost savings by increasing efficiency and reducing overall research costs
Time point accuracy
Increased accuracy of time points with longer walk away time for users

Example DMPK - Transporter assay workcells
No matter your goals or throughput needs, we can design and implement a solution to automate your DMPK - Transporter Assay workflow
Small workcell
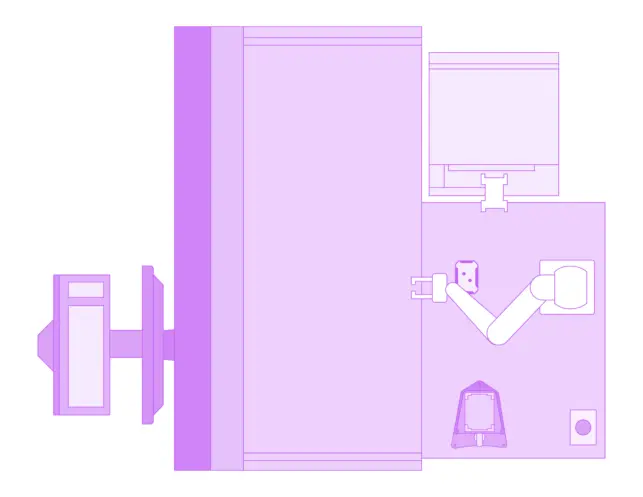
Small workcell
This small example workcell showcases the minimal instrumentation required to run a DMPK - Transporter assay. The design of this workcell moves the pipetting and liquid transfer needs to the liquid handler with fewer materials being stored off-line in static racks. This setup increases the user interaction points within the process but focuses on the more labor-intensive portion of process.
Feature details for Hardware
Hardware:
1x Robotic Arm (Precise PF400)
1x Liquid Handler (Tecan Fluent 780)
1x Incubator, 37C with 95% humidity and 5% CO2 (LiCONiC STX-44SA)
1x Random Access Plate Storage Hotel
Feature details for Software
Integration Software:
Green Button Go Scheduler with related Device Drivers
Feature details for Hardware
Hardware:
1x Robotic Arm (Precise PF400)
1x Liquid Handler (Tecan Fluent 780)
1x Incubator, 37C with 95% humidity and 5% CO2 (LiCONiC STX-44SA)
1x Random Access Plate Storage Hotel
Feature details for Software
Integration Software:
Green Button Go Scheduler with related Device Drivers
Medium workcell
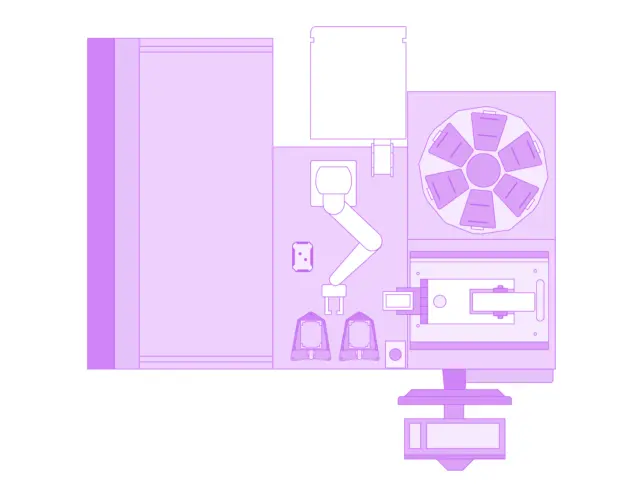
Medium workcell
Additional hardware means more functionality and walkaway time for labs running a DMPK - Transporter Assay. System hardware grows to a larger footprint due to the addition of more storage for ambient and incubation space, as well as the addition of sealing and reading capabilities.
Feature details for Hardware
Hardware:
1x Robotic Arm (Precise PF400)
1x Liquid Handler (Tecan Fluent 780)
1x Incubator, 37C with 95% humidity and 5% CO2 (LiCONiC STX-110SA)
1x Multimode Plate Reader (Agilent BioTek Synergy Neo2)
1x Plate Sealer, Optional (Azenta a4S)
2x Random Access Plate Storage Hotel
1x Automated Plate Storage Carousel (PAA CS-6)
Feature details for Software
Integration Software:
Green Button Go Scheduler with necessary Device Drivers
Feature details for Hardware
Hardware:
1x Robotic Arm (Precise PF400)
1x Liquid Handler (Tecan Fluent 780)
1x Incubator, 37C with 95% humidity and 5% CO2 (LiCONiC STX-110SA)
1x Multimode Plate Reader (Agilent BioTek Synergy Neo2)
1x Plate Sealer, Optional (Azenta a4S)
2x Random Access Plate Storage Hotel
1x Automated Plate Storage Carousel (PAA CS-6)
Feature details for Software
Integration Software:
Green Button Go Scheduler with necessary Device Drivers
Large workcell
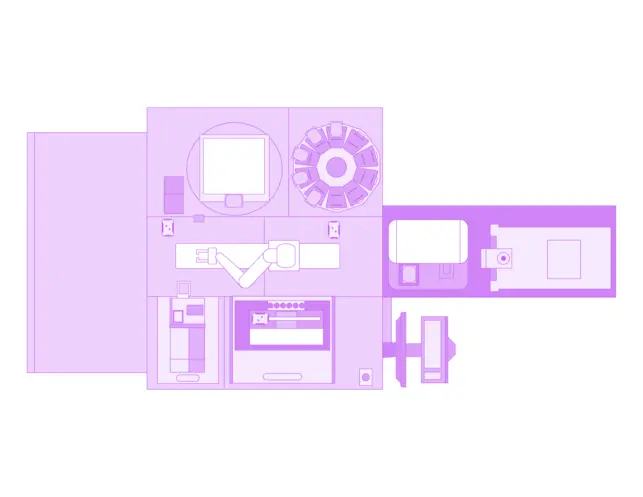
Large workcell
The large workcell example includes more front-end sample prep, additional analysis options while being able to miniaturize sample volumes. Incubator and consumable storage have been increased to support more parallel processing for assay plates. Workcell now performs plate labeling and data tracking for better sample traceability. Orchestrator modules allow for data to be linked to company data infrastructure for queuing and handling more actions within Green Button Go.
Feature details for Hardware
Hardware:
1x Robotic Arm (Precise PF400 on 1m Rail)
1x Liquid Handler (Hamilton Vantage 2.0)
1x Acoustic Small-Volume Dispenser (DISPENDIX i.Dot)
1x Plate Washer (Agilent BioTek EL406)
1x High-Volume Dispenser (Formulatrix Tempest)
1x Plate Sealer (Agilent PlateLoc)
1x Multimode Plate Reader (Agilent BioTek Synergy Neo2)
1x LC/MS/TOF Analytical Instrument (SCIEX Echo LC-MS/MS/Q-TOF)
2x Automated Lidding/Delidding Instruments (HiRes Biosolutions LidValet)
1x Plate Labeler (Agilent VCode)
1x Automated Plate Storage Carousel (PAA CS-10)
1x Incubator, 37C with 95% humidity and 5% CO2 (Thermo Cytomat 10C)
Feature details for Software
Integration Software:
Green Button Go Scheduler with necessary Device Drivers
Green Button Go Orchestrator
Feature details for Hardware
Hardware:
1x Robotic Arm (Precise PF400 on 1m Rail)
1x Liquid Handler (Hamilton Vantage 2.0)
1x Acoustic Small-Volume Dispenser (DISPENDIX i.Dot)
1x Plate Washer (Agilent BioTek EL406)
1x High-Volume Dispenser (Formulatrix Tempest)
1x Plate Sealer (Agilent PlateLoc)
1x Multimode Plate Reader (Agilent BioTek Synergy Neo2)
1x LC/MS/TOF Analytical Instrument (SCIEX Echo LC-MS/MS/Q-TOF)
2x Automated Lidding/Delidding Instruments (HiRes Biosolutions LidValet)
1x Plate Labeler (Agilent VCode)
1x Automated Plate Storage Carousel (PAA CS-10)
1x Incubator, 37C with 95% humidity and 5% CO2 (Thermo Cytomat 10C)
Feature details for Software
Integration Software:
Green Button Go Scheduler with necessary Device Drivers
Green Button Go Orchestrator

Best use cases for bringing in automation
Regular workflow schedules
Automation helps to guarantee uniformity and prompt outcomes
High throughput requirements
Automation is effective at managing substantial sample volumes
Busy lab personnel
Automation supports scientists who are engaged in tasks outside of the bench to allocate more time to essential activities
After-hours operation of the lab
Automation supports the ability to run a lab at any time of day or on the weekend
What to watch out for
Technical expertise required
Automation demands technical expertise to operate and maintain after deployment. Laboratories may need to invest in additional training for staff members or hire specialized personnel to support the automated systems.
Time to deploy
Implementing automation may require integration with existing laboratory information systems (LIS) and electronic record systems. Integration can take time.
Process standardization needed
Laboratories may need to modify existing processes, recertify, or develop new processes entirely to handle the new flow of data to fit together with automation.